Samp, the leading deeptech company behind Shared Reality, today announced the launch of its industry-first Copilot, a groundbreaking AI assistant designed to transform asset intelligence across piping-intensive industrial sites such as existing refineries, chemical plants, and power stations.
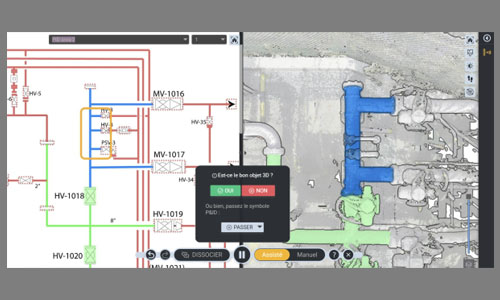
In many large, complex facilities, the accuracy and connectivity of infrastructure data remain a critical challenge. Limited visibility and outdated or incomplete legacy documentation hinder operational efficiency, safety, and capital investment decisions. Shared Reality’s Copilot addresses this longstanding issue by fusing advanced AI with a human-in-the-loop workflow, creating the first-ever platform empowering teams to seamlessly link 3D reality capture with technical data, P&IDs, and other legacy systems to create a fully verified, living digital twin.
“This is a new category of asset intelligence,” said Laurent Bourgouin, CEO and co-founder at Samp. “Shared Reality’s Copilot revolutionises how industrial teams capture and validate their existing facility data. By ending the data quality crisis that has long plagued the sector, we’re empowering organisations to operate safer and faster than ever before.”
Shared Reality automatically detects pipes, valves, pumps, and other critical assets within 3D scans or engineering drawings, making it easy to link them together. What sets this solution apart is Copilot’s human-in-the-loop verification process, where AI linking suggestions are reviewed and validated by users to ensure every connection is accurate and trustworthy. This collaboration between machine intelligence and human expertise produces a unified infrastructure model that integrates fragmented data sources and legacy documents.
Every verification step is logged to provide a traceable audit trail, supporting compliance, reporting, and future updates. Designed as a cloud-native, enterprise-ready solution, Shared Reality easily integrates with existing asset and maintenance management platforms, allowing continuous updates and engaging accessibility.
The business impact of Copilot is significant. It can reduce infrastructure verification time by up to 70%, while improving confidence in data connections by 90%. It enables early detection of undocumented changes, which can prevent costly rework. Moreover, it allows teams to make better-informed capital investment decisions, more efficient procurement, and shortens maintenance schedules, laying a solid foundation for digital twins and predictive operations.
Use cases for Shared Reality’s Copilot include generating accurate as-built models that reflect the real facility layout, improving maintenance planning with up-to-date system data, supporting turnaround events by quickly verifying current system status, facilitating regulatory compliance through precise documentation, identifying discrepancies between design and reality, optimising asset investment, and streamlining procurement by providing suppliers with reliable scope details.
Unlike traditional AI tools that operate as ‘black boxes’, Copilot’s human-in-the-loop approach ensures automation is balanced with expert oversight. This combination significantly reduces the risk of cost overruns, safety incidents, and regulatory exposure, making it a trusted tool for industrial operators.
Photo: SAMP